Wiki Languages: Ligurian language (Líguru)
| Language: Ligurian (Ligurian language) | Local name: Líguru |
| Language code: lij | Display language: Simple English (simple)|
| Speak area: Italy | Classification: Romance |
| Country: Italy | Second language: |
| Usage: regional | Wiki language for Ligurian language |
Dictionary for Ligurian (Líguru) in Simple English
| English | Ligurian |
| Líguru | Simple English |
| Ligurian / Genoese | |
|---|---|
| lìgure, zeneize/zeneise | |
| Pronunciation | ˈliɡyre, zeˈnejze |
| Native to | Italy, Monaco, France |
| Region | Italy • Liguria • Southern Piedmont • Southwestern Lombardy • Western Emilia-Romagna • Southwestern Sardinia France • Southeastern Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur • Southern Corsica |
Native speakers | 500,000 (2002)[1] |
Language family | Indo-European
|
Early forms | Old Latin
|
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | lij |
| Glottolog | ligu1248 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-oh & 51-AAA-og |
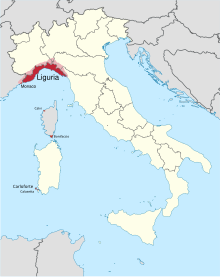 | |
Ligurian or Genoese (lìgure or zeneize) is a Romance language of the Gallo-Romance branch spoken in the Liguria region in northwestern Italy and in two communes in the Italian island of Sardinia as well as in parts of Alpes-Maritimes and Corsica in southeastern France, and in Monaco.
Ligurian belongs to the Gallo-Italic languages group within the Gallo-Romance branch and therefore differs significantly from standardItalian, which is spoken south of the La Spezia-Riminilanguage border; the same applies to the other northern Italian languages. They include Piedmontese, Lombard, Emilian and Romagnol.
Ligurian has many dialects, the most widespread of which is Genoese, spoken in Genoa. Another dialect of Ligurian, is Monegasque, which is spoken as a first language by the people of Monaco.
Status
The Ligurian language, like many minority languages, is an endangered language which is disappearing more and more in recent years and may be threatened with extinction.
Only around 500,000 out of the 2,000,000 Ligurians, speak Ligurian, who are mostly older people. Because the Ligurian language is rarely passed on to the younger generations, fewer younger people speak it. That is why like the other minority languages, it is slowly being replaced by standard Italian or standard French.
Ligurian does not enjoy an officialstatus in Italy. Hence, it is not protected by law.
Ligurian also does not enjoy an official status in France.
In Monaco, where it is known as Monegasque, it is not an official language, but it enjoys an official status and is taught in schools, where it is compulsory.
Dialects
Dialects of the Ligurian language are:
- Bonifacino (bunifazzin, in Bonifacio, Corsica, France)
- Brigasc (brigašc, in La Brigue, Alpes-Maritimes, France and Briga Alta, Liguria, Italy)
- †Figoun (in Provence, France)
- Genoese (zeneize or zeneise, main Ligurian dialect, spoken in Genoa, Liguria, Italy)
- †Genoese of Gibraltar (lìgure de Gibiltæra in Gibraltar)
- †Genoese of Tabarca (ligüre de Néùva Tabòrka, in Tabarca, Valencia, Spain)
- †Genoese of Portoria (zeneize pörtoriàn, in Genoa, Liguria, Italy)
- Intemelio (in Sanremo -sanremàscu- and Ventimiglia -ventemigliusu-, Liguria, Italy)
- Monégasque (munegascu, in Monaco)
- Novi dialect, part of Oltregiogo Ligurian (nuvàize, north of Genoa, mainly in Val Borbera and Novi Ligure, Piedmont, Italy)
- Royasc (ruiascu, in Upper Roya Valley, between Liguria, Italy and Alpes-Maritimes, France)
- Savonese (savuneise, in Savona, Liguria, Italy)
- Spezzino (spezin, in La Spezia and its province, Liguria, Italy)
- Tabarchino (tabarkin, in Calasetta and Carloforte, Sardinia, Italy)
- Tendasc (tendašc, in Tende, Alpes-Maritimes, France)
The † sign means that this dialect is extinct, meaning it has no speakers.
References
- ↑Ligurian / Genoese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Other websites
![]() Wikisource has original text related to this article: Ligurian language wikisource
Wikisource has original text related to this article: Ligurian language wikisource
- Associazione O Castello (in Italian and Ligurian)
- Académia Ligùstica do Brénno (in Ligurian)
- "Official Orthography and Alphabet" proposed by the Académia Ligùstica do Brénno (in Ligurian)
- GENOVÉS.com.ar (English version) – Ligurian language & culture, literature, photos and resources to learn Ligurian (in English)
- Ligurian basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical DatabaseArchived 2020-06-01 at the Wayback Machine
- The Firefox browser in Ligurian
- The Opera browser in Ligurian
