Wiki Languages: Hungarian language (Magyar)
| Language: Hungarian (Hungarian language) | Local name: Magyar |
| Language code: hu | Display language: Simple English (simple)|
| Speak area: Hungary | Classification: Uralic |
| Country: Hungary | Second language: |
| Usage: national | Wiki language for Hungarian language |
Dictionary for Hungarian (Magyar) in Simple English
| English | Hungarian |
| Magyar | Simple English |
| Hungarian | |
|---|---|
| magyar | |
| Native to | Hungary and areas of Austria, Croatia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Ukraine |
Native speakers | 14–15 million (2005)[1] |
Language family | Uralic
|
Writing system | Latin (Hungarian alphabet) Hungarian Braille |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Research Institute for Linguistics of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | |
| ISO 639-2 | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:hun – Modern Hungarianohu – Old Hungarian |
Linguist List | ohu Old Hungarian |
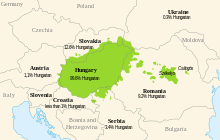 Regions of the Carpathian Basin where the Hungarian language is spoken | |
Hungarian is a Uralic language. The Hungarian name for the language is Magyar.
The Finno-Ugric languages also include Finnish, Estonian, Lappic (Sámi) and some other languages spoken in Russia: Khanty and Mansi are the most closely related to Hungarian. The Hungarian name for the language is Magyar.
Although Hungarian is not an Indo-European language, unlike most other European languages, its vocabulary has many words from Slavic and Turkic languages and also from German.
Speakers
Hungarian is spoken by approximately 13 million people. Most of them live in Hungary (around 10 million) and Romania (around 1.5 million), but there are also speakers in Slovakia, the northern part of Serbia (Vojvodina), Ukraine and other countries. Hungarian is the official language of Hungary and one of the official languages of the European Union (EU). It is also an official language of the Autonomous Republic of Vojvodina (Serbia) and of some places in the Republic of Slovenia.
Hungarian has several dialects, but people can easily understand one another. The Csángó dialect in Romania, however, is archaic and has changed less than the other dialects.
Hungarian literary language is based on the Northeastern dialect.
Although Hungarian is not an Indo-European language, its vocabulary has many words from Slavic and Turkic languages and also from German.
Austro-Hungarian
Austro-Hungarian (Össtereich-Ungarn dialekt, Ausztriai-Magyar nyelvjárás) is a dialect of Hungarian that inherited loanwords from German such as grammar structure, phonology and pronounciation, the language first spoken in the 1800's during the statehood of Austria-Hungary.
text in Hungarian and Austro-Hungarian
Hungarian;
Nem kell palota ahoz hogy boldog légy, nem kell pénz és gazdagság hogy minden embernek jót szívében millió csillag ragyog, s akkor leszel igazán boldog ha fényleni hagyod.
Austro-Hungarian;
Nem kell brauchst keinen hogy boldog zu sein, te brauchst kein pénz und gazdagság sein, um anderen Gutes tégy, eine ember hertze million csillag glücklich, du sie leuchten igazán boldog wenn fényleni lässen.
Today, there are an estimated 1.7 million people who can speak Austro-Hungarian near the Austrian and Hungarian border.
Grammar
Hungarian grammar is very different from that of Indo-European languages like English.
Hungarian has no grammatical gender. For example, there are no separate words for "he" and "she" but there is one pronoun (ő). Instead of prepositions, (like "from" or "with"), Hungarian uses suffixes (particles at the end of main words). For example, "from Budapest" becomes Budapestről, and "with Alexandra" becomes Alexandrával.
Another Hungarian feature is vowel harmony: suffixes change according to (harmonise with) the vowel of the main word. If they have a in the word, the suffix normally has a as well (fa "tree" and fával"with a tree"), and if they have e, the suffix will change to have e as well' (teve "camel" and tevével "with a camel").
Hungarian words have the accent on the first syllable.
Writing
The Hungarian alphabet is based on the Latin alphabet. Some letters have diacritics (dots or commas above them) and so Hungarian has 44 letters, more than the 26 of English.
Since Hungarian writing is mostly phonetic, it is easy to write words by knowing their pronunciation.
History
The earliest known written Hungarian words are to be found in a Latin document, the Foundation Charter of the Abbey of Tihany (1054). The Funeral Oration and Prayer (1192-95) and the Old Hungarian Lament of Mary (13th century) are the earliest known continuous Hungarian texts.
In the 16th century, the first printed Hungarian texts were published. The modern literary language appeared in the 18th and the 19th centuries.
Hungarian replaced Latin as the official language of Hungary between 1844 and 1849 and then again in 1867.
References
- ↑Fenyvesi, Anna (2005), Hungarian Language Contact Outside Hungary, Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing, p. 11, ISBN 9027218587.
Other websites
- Collection of Hungarian Dictionaries
- SZTAKI szótár
- Dicfor (DICtionary FOR you) szótár
